How to Treat Acne Effectively: Top Picks in Pakistan
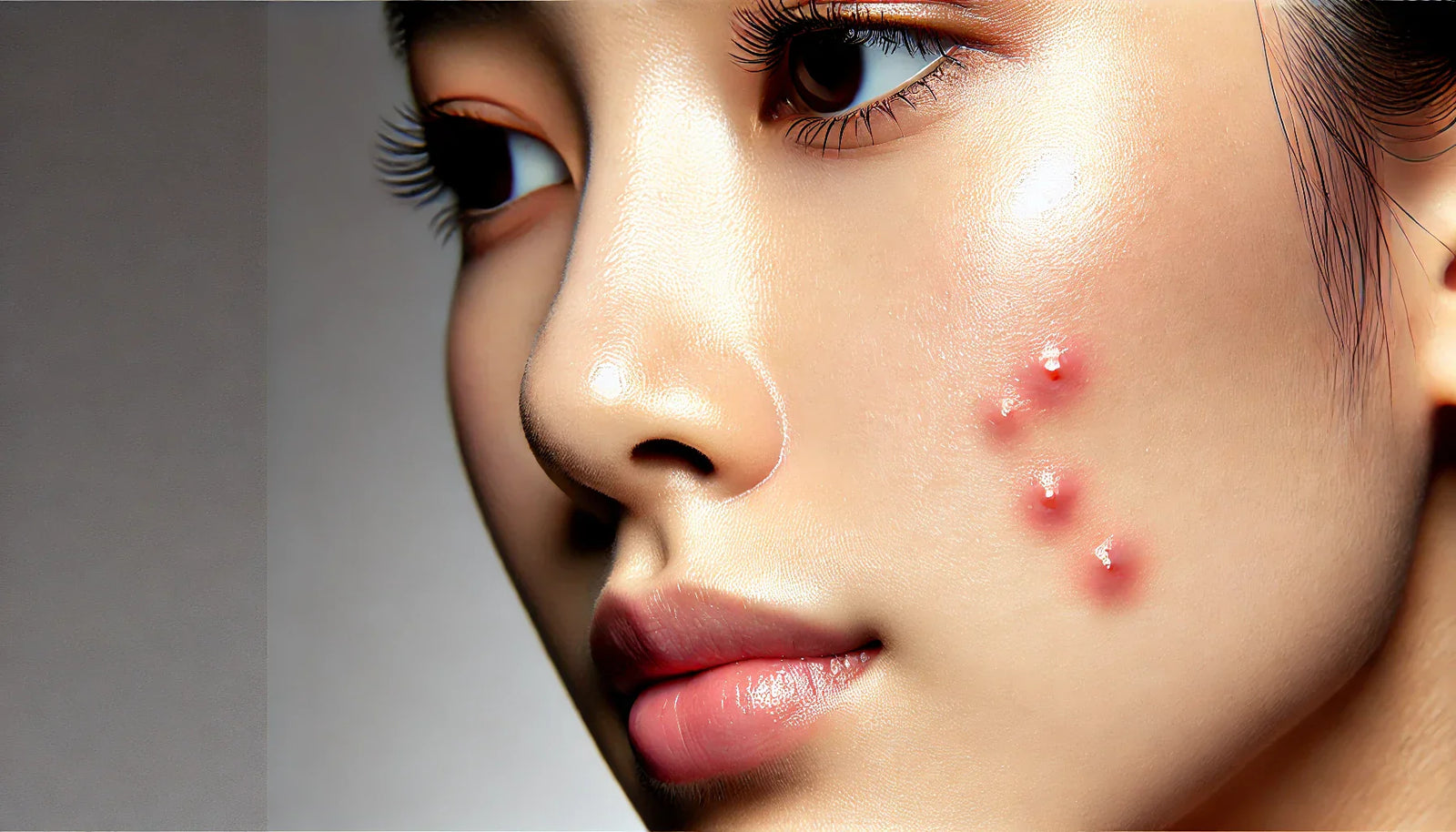
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to inflammation and blemishes. Acne can persist at any age, whether during teen years or adulthood, and it requires effective, tailored treatments. This article will explore the causes, types, and dermatologist-recommended treatments for acne, helping you understand how to manage and treat this condition effectively.
What Causes Acne?
Acne can be triggered by several factors, often acting together. Here’s a breakdown of the main causes:
-
Excess Sebum Production: Overactive oil glands can clog pores, leading to acne.
-
Dead Skin Cells: When dead skin cells mix with oil, they block the pores, causing breakouts.
-
Bacterial Growth: The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) can grow in clogged pores, causing irritation and inflammation.
-
Hormonal Fluctuations: Changes in hormones during puberty, menstruation, or stress can cause an increase in oil production, leading to acne breakouts.
-
Other Contributing Factors: Genetics, diet, and the use of comedogenic skincare products can also play a role.
Types of Acne and Recommended Treatments
There are several types of acne, each requiring specific treatments. Let’s look at the different types and how to treat them effectively:
1. Non-Inflammatory Acne (Whiteheads and Blackheads)
These are the mildest forms of acne and are caused by clogged pores. Whiteheads are closed pores, while blackheads are open pores filled with oil.
Recommended Treatment:
- Retinoids (Tretinoin or Adapalene): Helps promote cell turnover, which prevents clogged pores.
- Salicylic Acid: Helps exfoliate the skin and clear pores.
2. Inflammatory Acne (Papules and Pustules)
Inflammatory acne occurs when bacteria infect the clogged pores, causing redness, bumps, and pus-filled pimples.
Recommended Treatment:
Clindamycin Phosphate: A topical antibiotic that reduces bacterial activity and inflammation.
Benzoyl Peroxide: Targets bacteria and helps reduce redness.
3. Nodular and Cystic Acne
This is the most severe type of acne, causing deep, painful cysts or nodules beneath the skin. It may lead to scarring if left untreated.
Recommended Treatment:
- Oral Antibiotics (Azithromycin or Doxycycline): Reduces bacterial growth and inflammation.
- Tretinoin or Isotretinoin: Helps reduce severe acne and prevent scarring.
Should You Self-Treat Acne?
While mild acne can often improve with over-the-counter products, moderate to severe acne should be treated under the guidance of a dermatologist. Self-treatment for more serious forms of acne can often lead to delayed results, irritation, or worsening symptoms. If you have nodular or cystic acne, it is important to seek professional evaluation to avoid scarring and ensure proper treatment.
Dermatologist-Recommended Acne Treatments
1. Topical Treatments
- Tretinoin: A powerful treatment for all types of acne, it stimulates skin cell turnover, unclogs pores, and reduces inflammation.
- Clindamycin Phosphate: Reduces bacterial growth and inflammation. It is often combined with Benzoyl Peroxide for better results.
- Adapalene: A gentler retinoid ideal for mild to moderate acne. It reduces swelling and prevents clogged pores.
2. Oral Antibiotics
For moderate to severe acne, oral antibiotics can be helpful. They work by killing the bacteria responsible for acne and reducing inflammation.
- Azithromycin: Effective for reducing bacterial growth and inflammation.
- Doxycycline: Often used for stubborn acne.
These should be used only under the supervision of a dermatologist to prevent resistance or side effects.
Supporting Products for Acne-Prone Skin
To enhance your acne treatment, incorporating supportive skincare products can make a big difference.
Best Anti-Acne Face Washes:
These products cleanse the skin and help remove excess oil, dirt, and bacteria, providing a clean base for your acne treatment to work more effectively.
Sunscreen for Acne-Prone Skin: When using acne treatments like retinoids or antibiotics, your skin becomes more sensitive to the sun. Protect your skin with a non-comedogenic sunscreen to prevent sunburn and hyperpigmentation.
General Tips for Managing Acne
-
Wash Your Face Twice a Day: Use a gentle cleanser that is non-comedogenic to remove dirt and oil without irritating your skin.
-
Don’t Pick or Squeeze Pimples: Avoid squeezing pimples to prevent scarring and further irritation.
-
Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can promote clear skin.
-
Stick to Your Treatment: Acne treatments take time. Be patient and stay consistent. Results take 6–12 weeks to show.
Conclusion
Acne is a manageable condition with the right approach. From topical solutions like Tretinoin and Clindamycin Phosphate to oral antibiotics for severe cases, there are many treatment options available for every type of acne. Incorporate anti-acne face washes and sunscreen into your skincare routine to prevent future breakouts and protect your skin.
If you are struggling with persistent acne, don’t hesitate to consult a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan. With the right treatment and skincare routine, achieving clear, healthy skin is possible.